
The AI Productivity Revolution: How US Workflows Are Being Rewritten
AI-powered search engines and productivity tools are rapidly shifting from experimental add-ons to core workplace infrastructure in the US. Employees now depend on AI assistants to summarize documents, generate code, search internal knowledge bases, and automate routine tasks. Built on large language models and advanced retrieval systems, these tools convert natural-language prompts into actionable outputs that directly impact how work is planned, executed, and measured.
US Market
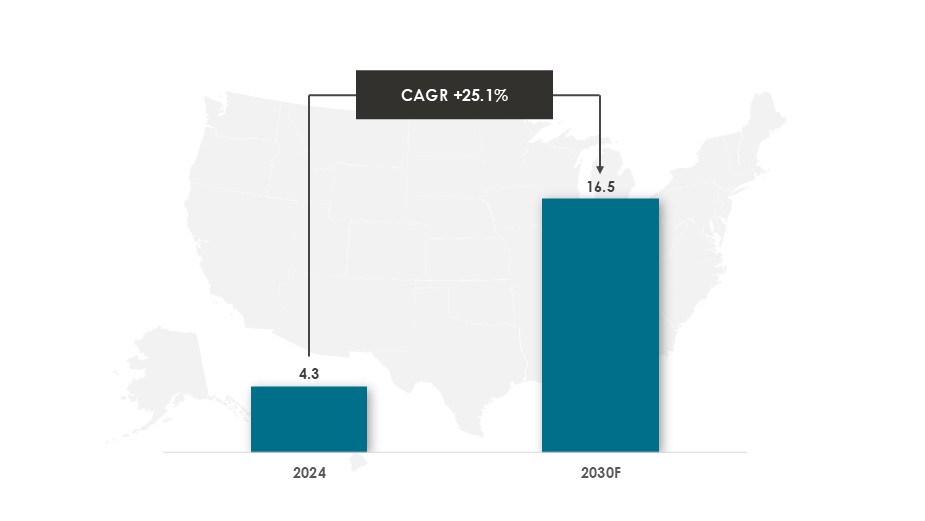
In 2024, the US held a dominant market position in the global AI productivity tools market, capturing around 43% share of the market.
In 2024, the US AI Productivity Tools market was valued at $4.3 billion and is expected to grow and reach to $16.5 billion by 2030.
Key Drivers: The US AI Productivity Tools market will be growing at an approximate CAGR of 25.1% during the forecasted period.Key Drivers: In the US, the growth of AI productivity tools is driven by advanced technology infrastructure, widespread cloud adoption, and strong venture capital support. Robust corporate R&D budgets fuel innovation, while leading tech giants and AI startups drive continuous improvement of platforms and user applications, strengthening the US’s leadership in AI.
Market Trends and Statistics
AI Use in the Workplace Rises Sharply
As AI capabilities evolve rapidly, a growing number of Americans are incorporating the technology into their daily work.
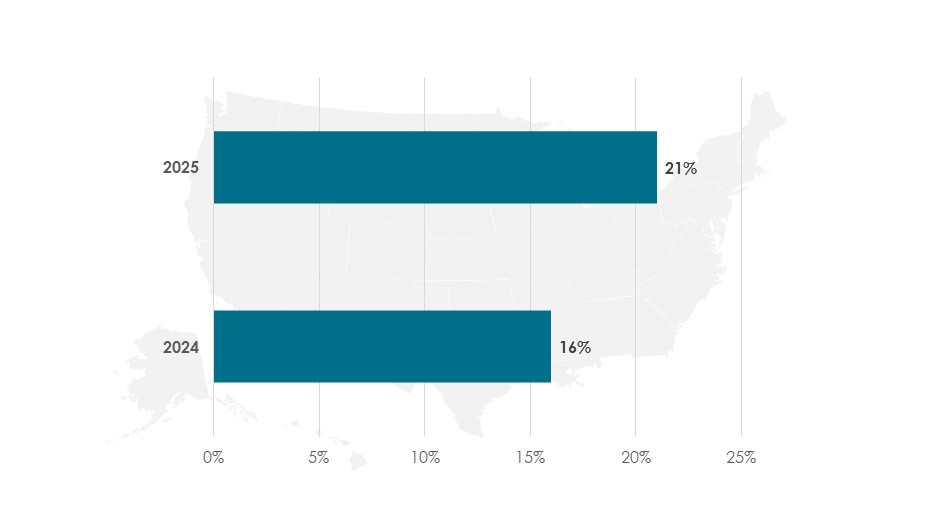
According to Gallup, around 27% of white-collar employees frequently use AI at work. According to a 2025PewResearchCenter survey, 21% of US workers (1 in 5) now use AI for at least part of their job – up from 16% in 2024.
Adoption and Training Gaps
Several surveys show that many employees use tools such as ChatGPT or Gemini without formal approval or training. One US workplace study reported that 74% of full-time employees use AI tools on the job, yet only 33% have received formal training on safe and effective use. This boosts local productivity but raises significant governance and data protection concerns.
AI Use and Higher Earnings
Artificial intelligence isn’t just changing how people work – it’s changing how much they earn. A new Nexford University survey shows that US professionals who use AI daily earn 40% more than those who don’t. Yet only 27% of employees say their company has offered AI training. This results in a widening divide between AI-fluent workers and those being left behind.
AI Use and Higher Earnings
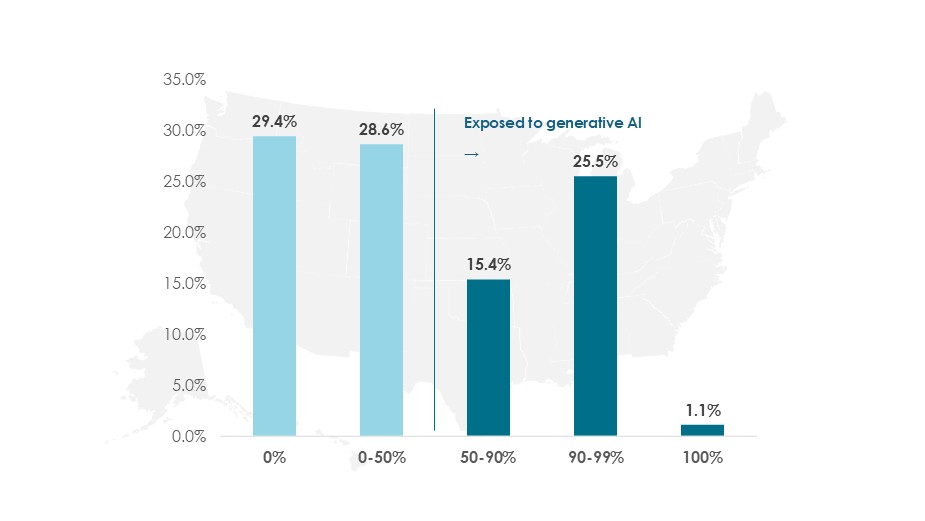
According to the distribution of US employment by AI-driven automation potential, following the task classifications of Eloundou et al. (2024), 29.4% of jobs have no meaningful substitution potential. 28.6% could see less than half of their tasks automated. Only about 1.1% of jobs are fully exposed, meaning AI could perform all required activities without significant human oversight. However, for more than a quarter of US roles, AI could handle 90–99% of tasks with only minimal supervision.
Conclusion
AI search engines and productivity tools are reshaping US workplaces, altering how employees find information, draft content, code, and collaborate. Spending, adoption, and time savings are rising quickly, especially in knowledge-intensive sectors, but gaps in training, governance, and measurement persist. Organizations that integrate responsible policies with targeted investment in AI-enabled workflows are best positioned to capture the most significant productivity gains in the decade ahead.
Data Sources: Market.us, DataBridge, Lifewire, Bank for International Settlements
Other Market Insights

